The security of crypto wallets has been a question mark for some time. And now, there's a Windows vulnerability leaving users infected with a previously unknown infostealer that's draining crypto wallets. It's called Phemedrone Stealer and malicious campaigns are exploiting this Windows vulnerability to steal crypto wallet contents and other sensitive information from victims.
What Phemedrone Stealer Steals
Although Microsoft released a patch (CVE-2023-36025) late last year, malware campaigns using Phemedrone Stealer accounted for the vulnerability in their attacks. The attackers use malicious .url files to download and exploit the vulnerability that bypasses checks and warnings from Microsoft Defender.
Just some of what Phemedrone Stealer actually steals includes: Data from crypto wallets like Bytecoin, Armory, Electrum, and Guarda; Passwords, autofill, and other data from chromium-based browsers like Microsoft Authenticator, Google Authenticator, LastPass, and Duo Mobile; Operating system information; and screenshots of whatever they want to.
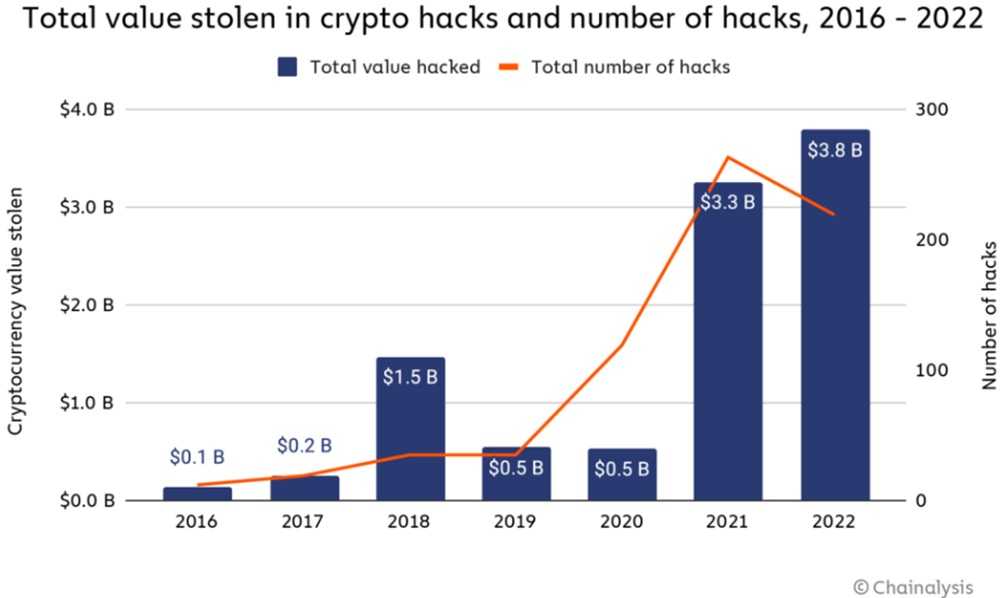
No one is quite sure how much Phemedrone Stealer has stolen from crypto wallets. But according to De.Fi, $2 billion was hijacked from these wallets last year. It's safe to say Phemedrone Stealer played a part in that massive total and will continue to pilfer crypto from unpatched devices. The cyber-smart answer to avoid this sneaky infostealer is immediately applying the security patch available and be sure to keep all of your devices up-to-date at all times.
Realst Malware Preying on Mac Users Through Fake Blockchain Games
Published September 9, 2023
A new cybersecurity threat has surfaced, ominously dubbed "Realst." Primarily targeting Mac users, this threat lurks in seemingly inconspicuous blockchain games. However, instead of a fun gaming experience, this malware is programmed to steal your personal data. Realst takes a smart, but deceitful approach to get to you, even looking to the future. If you play this game, they may be able to install Realst on your Mac and allow the hackers to choose their targets.
Ransomware Kicking And Punching Its Way To Kombat You
Published March 12, 2023
There is yet another example of how cybercriminals and their tools do not discriminate against the size of a company or the industry. This particular ransomware, that’s been punching its way around the globe since December is knocking out all in its tracks. It also creatively uses video game affiliations in its attacks. Cisco Talos researchers found ransomware that uses images of the popular game Mortal Kombat in the ransomware notes it leaves behind.
Google And Windows Sunsetting-Update Now
Published November 9, 2022
Without great fanfare, Google has announced that in February 2023, users of Windows Versions 7, 8, and 8.1 will stop receiving support for their version of Google Chrome. The dwindling numbers of users and the rapidly aging code used in these versions of Windows have put the final nail in the coffin for users who have become accustomed to Google updates and other forms of support. Google will opt out of supporting these older Windows versions when it releases the stable and market-ready version of Chrome 110.
Laundering Cryptocurrency: Hackers Claim Old School Tactics Still Work Best
Published October 20, 2022
If what a hacker does with a large pile of stolen cryptocurrency is the question, then laundering it, much like the way it’s done with illegal drug money and traditional financial heists, is the answer. Large-scale financial cybercrime, it seems, follows the roadmap that other more traditional financial crimes have used for decades to hide the haul. A recent report by SWIFT, a company that safeguards the global financial ecosystem, sheds light on the problem of large-scale money-laundering that stolen cryptocurrency creates.
Google Hit With 6th Zero-Day Vulnerability in Chrome in 2022. Update Chrome Now
Published September 6, 2022
Some days are better than others and Google has certainly had some better days than of late. On the heels of at least 5 other zero-day vulnerabilities in 2022 alone, there is another one that requires attention of users. This one is rated as a high-severity security issue and is noted as CVE-2022-307. Google has stated it isn’t releasing many details until the majority of users are supplied with the patch. Fortunately, it's already being issued.