Meerkats Shapeshift to Steal Logins
May 4, 2025
Morphing Meerkat is a recently identified phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platform that employs advanced techniques to deceive users and steal credentials. Discovered by cybersecurity firm Infoblox, this platform exploits Domain Name System (DNS) mail exchange (MX) records to dynamically generate fake login pages, impersonating over 100 brands, including Gmail, Outlook, AOL, Office 365, and Yahoo.
The attack initiates when a victim clicks on a malicious link embedded in a phishing email. Eventually, the click leads the victim through compromised domains to the final phishing site. Once there, the phishing kit determines the email domain being used. This process determines the victim's email service provider, enabling the kit to present a counterfeit login page that closely resembles the legitimate one, complete with the user's email address pre-filled to enhance authenticity, and simplify it for the user.
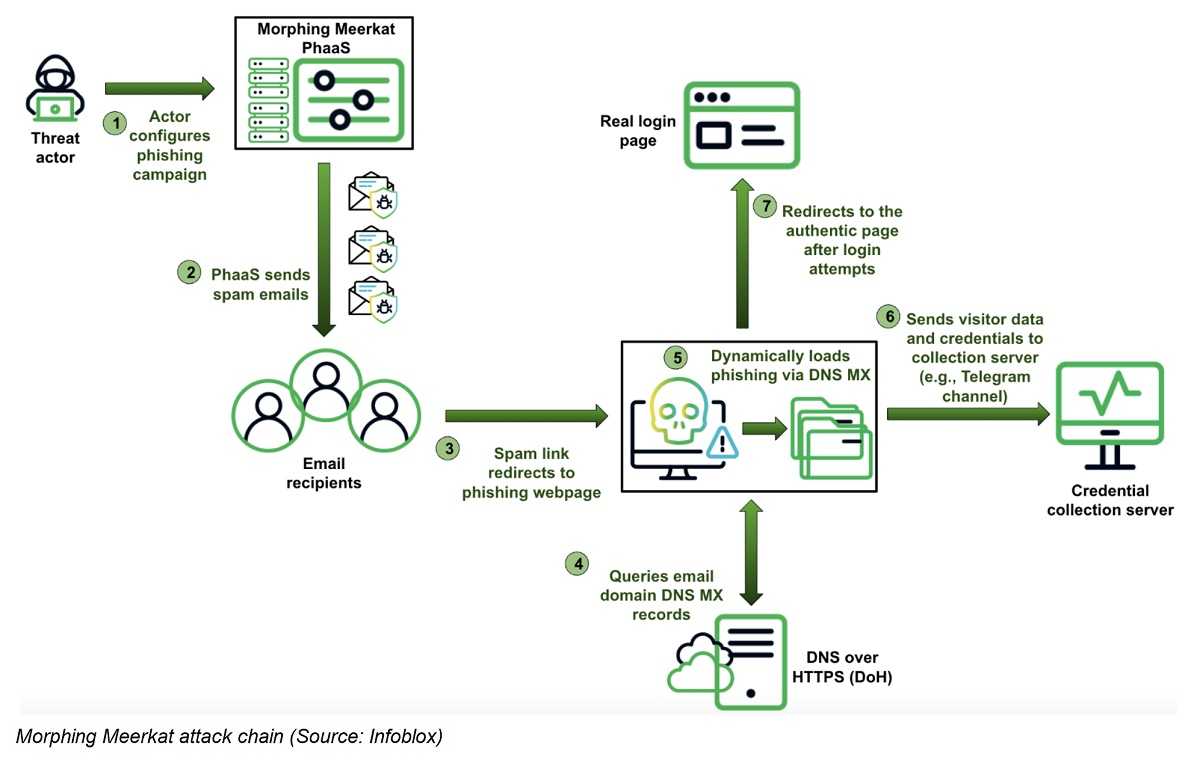
Morphing Meerkat's manages to conceal its DNS queries within encrypted HTTPS traffic, making detection challenging for traditional security tools. Additionally, the platform can dynamically translate phishing content into multiple languages, broadening its reach and effectiveness globally. Stolen credentials are distributed through various channels, including email and chat services like Telegram.
The emergence of Morphing Meerkat underscores the evolving sophistication of phishing operations and the necessity for robust cybersecurity measures. Organizations are advised to implement deep DNS logging and analysis, monitor for brand impersonation, deploy zero-trust email and web gateways, provide comprehensive user awareness training, and enforce strict email authentication policies such as DMARC, DKIM, and SPF to mitigate such threats.
For users, always be aware of phishing tactics, such as messages with a sense of urgency or punishment. Misspellings and bad grammar, links or attachments that are not expected or are from unfamiliar sources are still clues to phishing. Always pay close attention to the spellings of URLs, watching closely for the use of numbers in place of letters and other subtle changes.